Understanding Diabetes: Insights from a CMC Endocrinologist

Hello, everyone! I’m Dr. Lauren Buehler, one of the endocrinologists here at CMC Endocrinology. I’ve always been passionate about empowering my patients with the knowledge to help them better manage their diabetes diagnosis.
Today, I’d like to take the opportunity to go a little more in-depth and shed some light on insulin resistance, diabetes basics, and the treatments available to manage this condition. If you’re living with diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, this information will offer valuable insights, answer some common questions about your treatment options, and hopefully help facilitate more valuable conversations with your endocrinologists and primary care providers.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, damage to blood vessels, vision problems, kidney issues, and nerve damage. In the U.S. alone, over 37 million people live with diabetes, and the numbers are rising globally. Alarmingly, one in five people with diabetes is unaware they have it. Early detection and management are crucial to preventing these severe complications.
The Basics of Diabetes and Insulin
To understand diabetes, it’s helpful to know how insulin functions in the body. Normally, when you eat carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose (sugar) and enter the bloodstream. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, acts as a key, allowing glucose to enter cells and be used for energy.
Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin. This type is usually diagnosed in childhood but can occur later in life.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes is more common and involves insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin. Although the pancreas still produces insulin, it’s not used effectively. If you are type 2, your pancreas still works and makes the hormone insulin but you’ve developed resistance to insulin so the cells that are the target for the sugar are not able to use the insulin effectively to get the sugar from the bloodstream inside the cell to be used for energy.
I like to use the analogy of a key and a door to demonstrate the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. If insulin is the key to the door, with type 1 diabetes you don’t have the key to get inside the door. With type 2 diabetes, you have the key (insulin) but it doesn’t fit in the lock so you’re not able to use it correctly.
Treatment Options for Diabetes
Insulin Therapy
For those who need insulin, it can be administered via insulin pens or vials. Insulin is injected into the fatty layer of the skin. The goal is to mimic the pancreas’s normal function:
- Basal Insulin: Long-acting insulins (e.g., Levemir, Lantus) provide a steady level of insulin throughout the day.
- Bolus Insulin: Short-acting insulins (e.g., Humalog, Novolog) are taken before meals to manage the spike in blood sugar after eating.
In Type 1 diabetes, insulin is essential as the body doesn’t produce any. For Type 2 diabetes, insulin might be introduced if other treatments are insufficient.
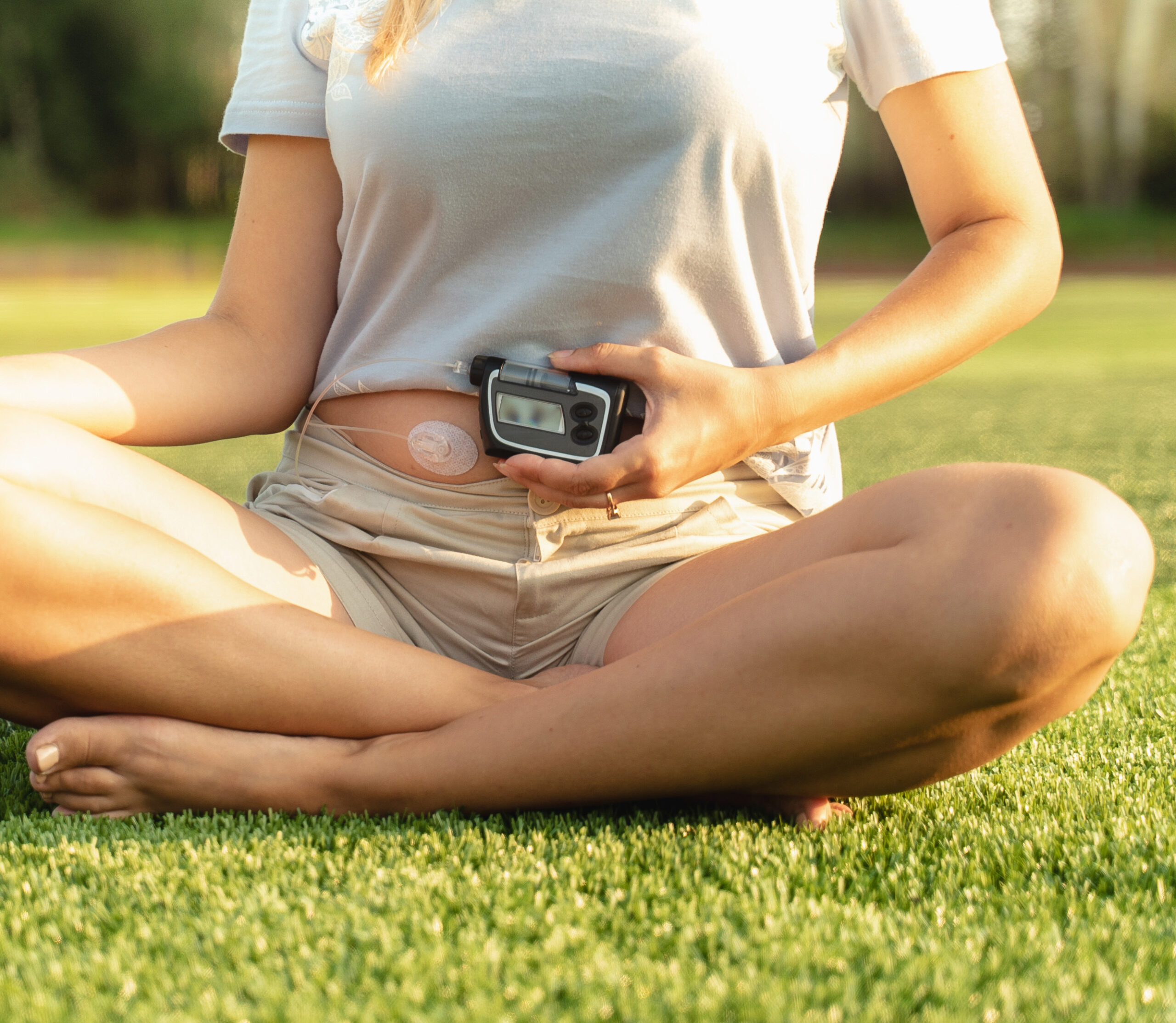
Insulin Pumps
Another option for insulin delivery is an insulin pump. These devices are particularly useful for people with Type 1 diabetes but can also be used in Type 2 diabetes patients, especially those on multiple daily injections. Insulin pumps (like the Omnipod, Medtronic, and Tandem) deliver insulin continuously through a catheter or a pod placed on the skin. Despite their convenience, pumps require regular interaction, including carbohydrate counting, dosing adjustments, and monitoring. They can provide more flexibility and precise control over insulin delivery compared to multiple daily injections.

Oral Medications
- Metformin: Often the first-line treatment for Type 2 diabetes, Metformin reduces insulin resistance and lowers liver sugar production. It’s effective but may cause gastrointestinal side effects in some patients.
- Sulfonylureas: Medications like Glipizide and Glyburide help increase insulin production from the pancreas but can lead to low blood sugar and are usually avoided in patients with severe kidney issues.
Newer Medications
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These injectables (e.g., Ozempic, Mounjaro, Trulicity) help with weight loss and provide cardiovascular benefits. They are typically administered weekly.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: Oral medications like Januvia improve blood sugar control but might have some GI side effects.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Some patients use Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) like the Libre or Dexcom. These devices are small sensors attached to the skin, often on the arm or abdomen, that measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid (the fat under your skin). CGMs provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, reducing the need for frequent finger pricks. They can alert you if your blood sugar is dropping too low, which helps prevent severe hypoglycemic episodes.
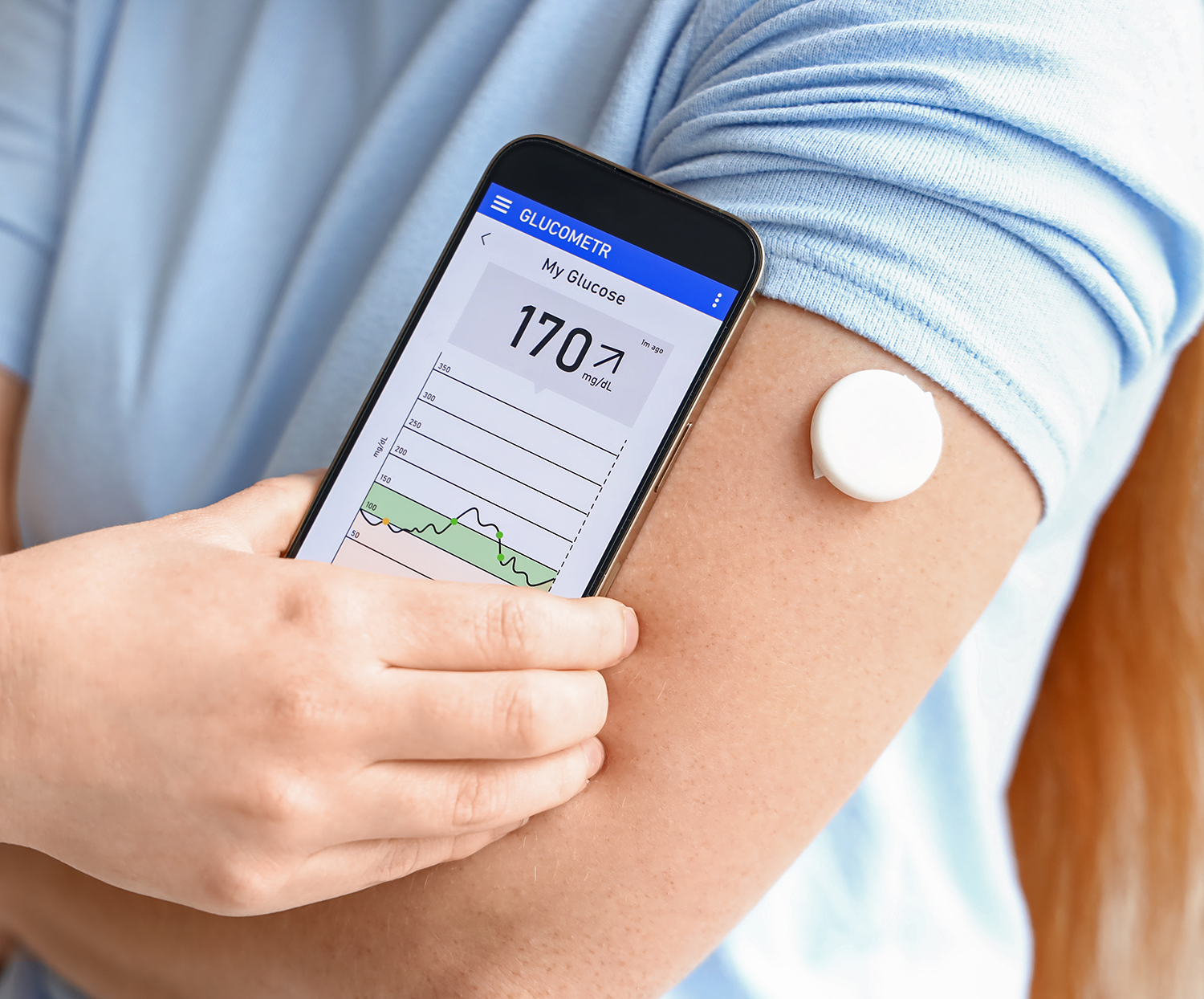
Additionally, CGMs are valuable for healthcare providers because they can download detailed data from the device, allowing us to see glucose trends minute by minute, including overnight, without needing to do multiple fingerstick tests.
Medical and Surgical Weight Management
For patients struggling with obesity, which is often linked to Type 2 diabetes, there are options for medical and surgical weight management. Medications such as GLP-1 receptor agonists can aid in weight loss. In some cases, surgical options may be considered for more substantial weight management. CMC Weight Loss offers a variety of medical and surgical weight loss options that have provided positive results for patients with a variety of medical conditions.
Take our FREE online seminar!
Your weight loss journey begins here.
Setting Treatment Goals
At CMC Endocrinology, our primary goal is to manage blood sugar levels effectively. The target A1C level for most patients is below 7%. However, for older adults, we may adjust this target to minimize the risk of low blood sugar. Regular monitoring of fasting and post-meal blood sugars is essential, alongside managing blood pressure and cholesterol to reduce cardiovascular risks.
Preventing and Managing Low Blood Sugar
Balancing blood sugar levels is crucial. Symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) include shakiness, sweating, dizziness, and confusion. Severe cases can lead to loss of consciousness or seizures. To manage low blood sugar, follow the 15-15 rule: consume 15 grams of carbohydrates, wait 15 minutes, and check your sugar level. If it remains low, repeat the process.
For those at risk of severe hypoglycemia, we may prescribe glucagon—a hormone that helps raise blood sugar levels in emergencies.
Comprehensive Diabetes Care
Managing diabetes involves more than just controlling blood sugar. Regular check-ups should include:
- A1C Testing: Every three to six months.
- Retinopathy Screening: Annual eye exams to check for vision problems.
- Foot Exams: Regular checks to prevent complications.
- Kidney Function Tests: To monitor potential kidney issues.
Vaccinations are also vital as diabetes can increase the risk of infections and complications from illnesses like the flu and COVID-19.
Effective Diabetes Management in Myrtle Beach
Managing diabetes effectively requires a multi-faceted approach, including understanding the disease, using appropriate medications, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle. If you’ve been diagnosed with diabetes, the first thing to do is see a qualified and trustworthy endocrinologist with a wealth of experience treating individuals with your condition. Diabetes is a complex condition that requires careful management and ongoing support. Through proactive measures, such as early detection, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical supervision, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their diabetes.
Our team at CMC Endocrinology remains dedicated to empowering our patients with the knowledge and resources needed to live well with diabetes. If you live in Myrtle Beach and the Conway area, we are the doctors for you. Specializing in treating type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, we are excited to offer top-notch endocrinology treatments and diabetes management options.
If you have any questions about your diabetes management or treatment options, feel free to reach out to our office. Call 843-234-9700 for more information about our practice and the physician referral process. We’d be honored to help you.





